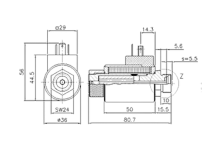
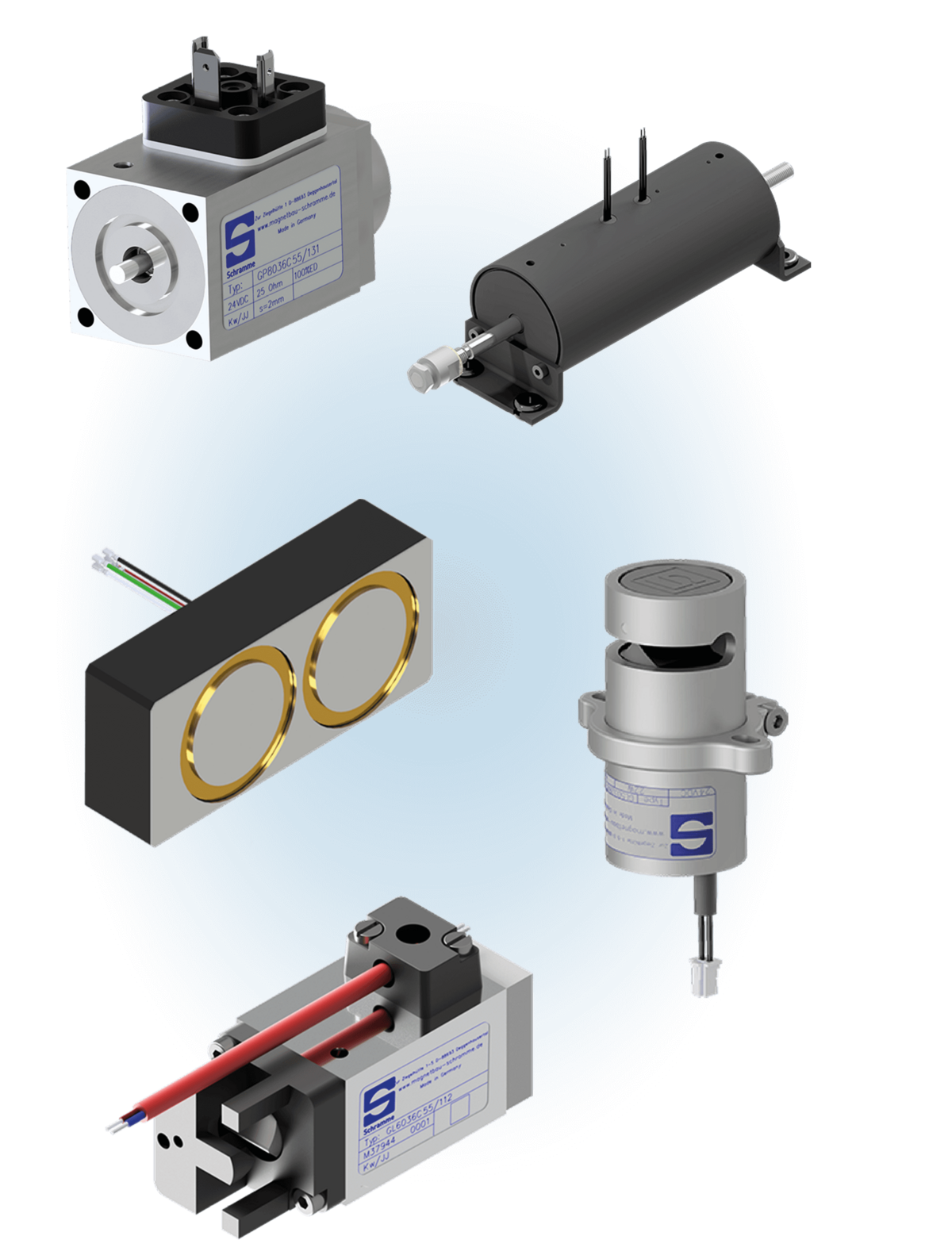
Solenoids
Solenoids are developed customer spezific and produced in series by Magnetbau Schramme. You can rely on our many years of experience and expertise to make your project a success.
Discover a diverse selection of different types of solenoids below.
Solenoids - Details
Advantages & types of Solenoids
Magnetbau Schramme has been developing and producing electromagnetic products in small and large series for a wide range of applications and industries for half a century. Solenoids are primarily used as actuators to generate linear and rotary movements.
There are various types of electromagnetic products, including typical linear solenoids, which generate a linear movement by attracting a movable magnetic armature. Holding solenoids hold metallic objects by generating a strong, persistent magnetic field. Solenoid valves are special solenoids that are used in hydraulic and pneumatic applications. The position of a valve is controlled by the movement of the armature, thus regulating the flow rate or pressure of liquids or gases. Other electromagnetic products include electromagnetic clutches and brakes, coils, actuation systems and magnetic bearings.
Please note
Please note that we do not have any standard products. The following linear solenoids are merely examples of customer projects realised in series.
Electromagnetic products: Industry sectors
Our industry diversity
Electromagnetic products have important functions in many industries: In safety technology, for example, they ensure reliable door locking systems, while in commercial vehicles they are used to support steering units.
Our management system in accordance with ISO 9001 & IATF 16949 helps us to ensure that quality requirements are met during the development and production of electromagnetic drives.


Marco Kiene
Management | CSO
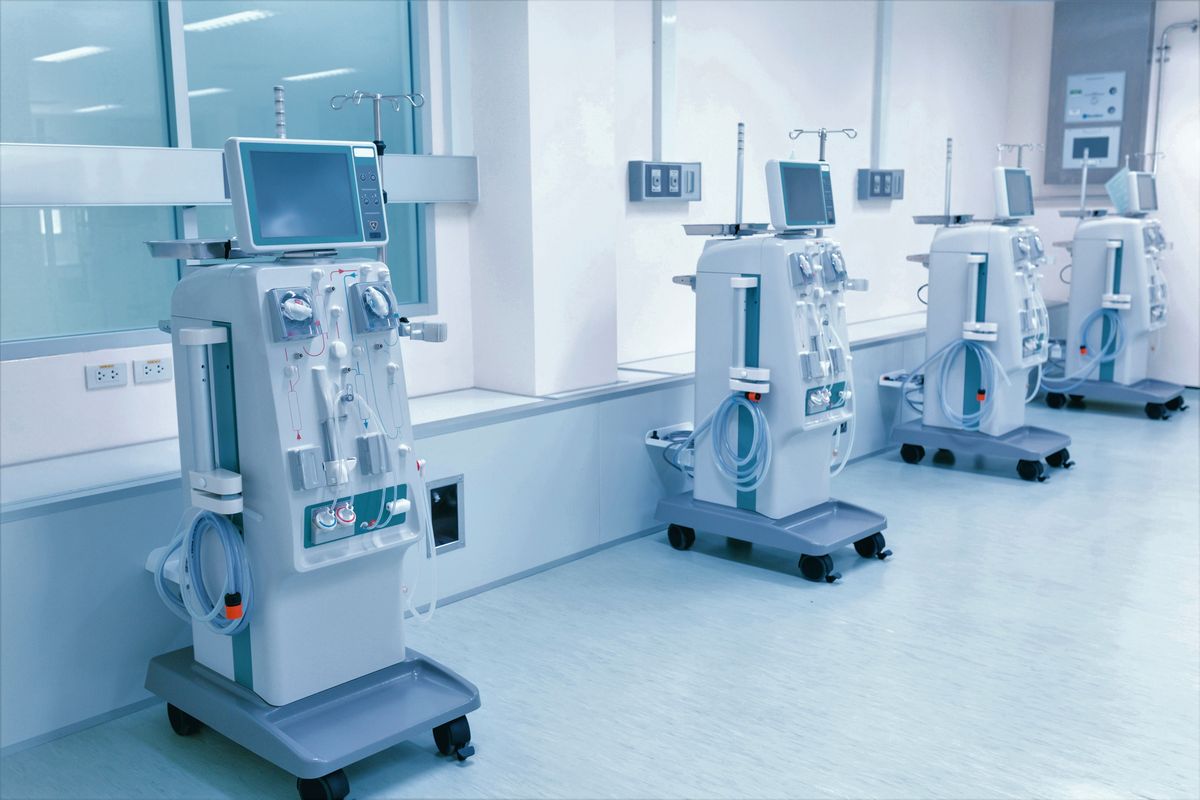
Solenoid application example
Lung ventilator
A lung ventilator supports breathing by pumping oxygen into the lungs and thus enabling gas exchange. Electromagnets, especially compact solenoids, play an important role here: they regulate the supply and removal of air and control the drive mechanism of the device. As a result, the air supply can be precisely controlled and the patient's ventilation can be organised efficiently and evenly.
More information about Solenoids
Electromagnets consist of a wire coil, which is often made of copper wire with an insulating coating, and a core made of ferromagnetic material such as iron or steel. The number of windings (coils) and the amperage determine the strength of the magnetic field generated. The core increases the usable magnetic field by focussing the magnetic flux density. Electromagnetic products can generate a magnetic field that can be switched on and off and its strength can be controlled by changing the current. Typical applications require voltages from a few volts to several hundred volts and currents ranging from milliamperes to several amperes. Electromagnets are manufactured in a variety of shapes and sizes to meet the specific requirements of the application.
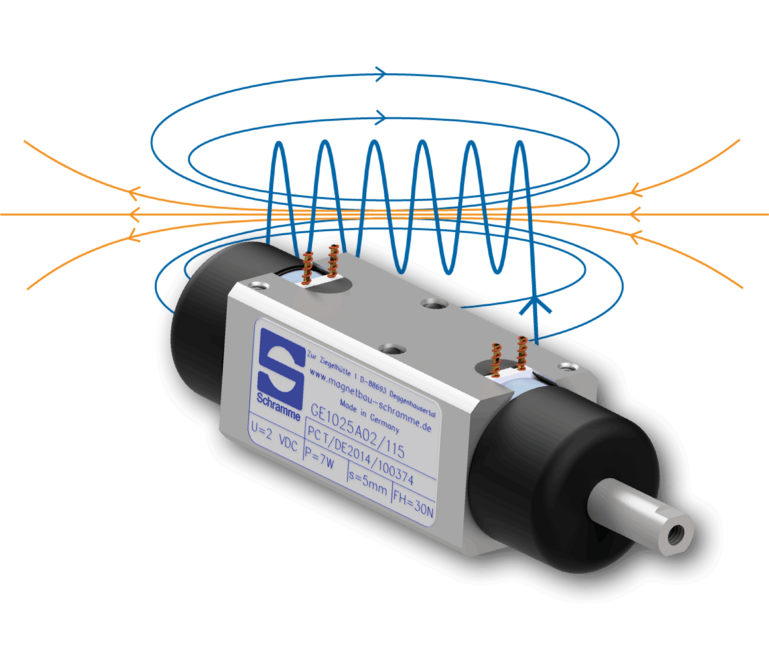
Structure of an electromagnet
- Housing: The housing of an electromagnet is usually a frame made of a ferromagnetic material such as iron or steel. It surrounds the magnetic core, encloses the coil of the electromagnet and serves to guide the magnetic field by maintaining the flow of the magnetic field lines and preventing the magnetic field from spreading in undesirable directions. The housing also protects the coil from external influences such as vibrations, moisture or damage.
- Coil: The coil usually consists of a wire winding with a magnetisable core in the centre. The wire used for the coil is usually made of a highly conductive material such as copper. The number of windings in the coil, the current strength and the shape of the coil influence the properties of the magnetic field generated.
- Armature: The armature is the movable component that strives for the ideal state of the iron circuit when the electromagnet is energised, i.e. it minimises the working air gap and thus moves towards the iron core.
- Ironcore: The iron core is the stationary part in the electromagnetic product towards which the armature moves when the coil is energised.
- Electrical connection: The electrical connection of electromagnets is crucial for their reliable operation and safe integration into an overall system. Depending on the application and design, there are different types of electrical connections that are used for electromagnets.
Advantages of electromagnets
A major advantage of electromagnets is their strength. Significantly greater magnetic forces can be applied with an electromagnet than with classic permanent magnets. This makes them ideal for applications that require a high magnetic force.
Electromagnets are also characterised by their versatility. They are used in a wide range of applications. From excavators to church organs, from escalators to drilling machines, from lorries to summer toboggan runs - magnetic technology can be found almost everywhere.
Controllability is also an advantage, as electromagnets can be controlled precisely and quickly, making them ideal for applications where fast and accurate control of magnetic force is required.
Another strength of electromagnets is their efficiency. They only consume power when they are switched on. In combination with permanent magnets, magnetic forces can even be used without current and eliminated when energised.
Summary: What are the biggest advantages of electromagnetic systems and magnet technology?
- Robust design and low sensitivity to interference
- Fast movement with high dynamics and large forces
- Low technical complexity compared to other technical solutions
- Simple electrical control
- Wide operating temperature range
- Small number of moving parts
- Long service life and no maintenance required
- High protection classes and explosion-proof products
- Can be used in a wide variety of areas
Solenoids - Questions & Answers
How does an electromagnet work?
Electrical energy is converted into magnetic energy and then into mechanical energy. Current flows through the copper coil, creating a magnetic field. As the elements, iron core and housing are made of ferromagnetic material, they try to create an ideal magnetic circuit when a magnetic flux passes through them. This means that materials with low permeability, such as air, are avoided. The armature therefore tries to close the air gap and moves in the direction of the iron core. Electromagnets are mainly used as drive elements to generate linear and rotary movements.
What is the difference between an electromagnet and a permanent magnet?
The difference between an electromagnet and a permanent magnet is the way in which the magnetic field is generated: An electromagnet only generates a magnetic field when an electric current flows through a wire coil, so that its magnetic field can be switched on and off and its strength can be varied. A permanent magnet, on the other hand, permanently generates a constant magnetic field without the use of electrical energy and cannot be switched off.
On which parameters does the force of an electromagnet depend?
The force of an electromagnet depends on several parameters, including
- Number of windings of the coil: The more turns the coil has, the stronger the magnetic field is generated, which leads to a greater force.
- Amperage: The higher the current flowing through the coil, the stronger the magnetic field and therefore the greater the force.
- Size of the magnetisable core: A larger core generally means a stronger magnetic field and therefore a greater force.
- Current strength + number of turns: The product of current strength and number of turns influences the field strength and therefore the magnetisation via the iron circuit and therefore the magnetic force.
How are electromagnets produced?
The production of electromagnets involves several precise manufacturing steps: Firstly, all components that form the magnetic circuit are manufactured. These can be produced by machining or moulding. If pressure-tightness is required, non-magnetic elements are joined by welding and soldering. Components from which the actual copper coil is produced are usually manufactured using plastic injection moulding. This often results in a coil former around which the wire is then wound. The coil produced in this way is later encapsulated or overmoulded with plastic for protection and insulation. All components are then assembled. After assembly, each electromagnet is tested for functionality in the end-of-line test and then securely packaged.
What role does the magnetic material of the armature play in switching behavior?
Materials with low coercive field strength (e.g., soft iron) enable fast switching operations but tend to saturate at high magnetic fields. Materials must be specified depending on dynamics, power requirements, and temperature behavior.
In which environmental conditions are electromagnets used?
Electromagnets are used in a wide range of environmental conditions, including industrial plants with high temperatures, high humidity and dusty atmospheres. They are also used in extreme environments such as vacuum chambers, extremely cold temperatures or maritime environments with a high concentration of salt water. They are also used in potentially explosive areas, such as in the chemical and oil industries, where special protective measures against sparking are required.
What does hysteresis mean for an electromagnet?
In the case of electromagnets, hysteresis means that the material in the magnetic circuit always has residual magnetism after magnetisation. This residual magnetism influences the performance of electromagnets when they are actuated again. This hysteresis can therefore affect the efficiency, control quality and response times of electromagnets. Especially in applications where frequent and rapid magnetic field changes are required, the effect of hysteresis must be taken into account when designing and dimensioning electromagnets. There are design principles that minimise hysteresis effects or even make them unrecognisable.